

Natural diffraction gratings occur in the feathers of certain birds. Figure 4 shows idealized graphs demonstrating the sharper pattern. That is, their bright regions are narrower and brighter, while their dark regions are darker.
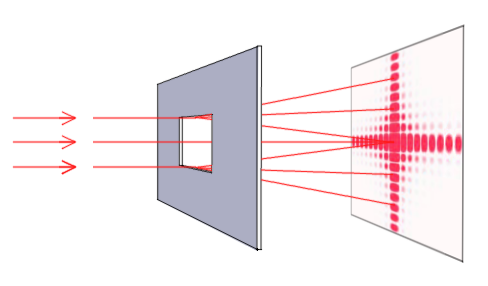
What makes them particularly useful is the fact that they form a sharper pattern than double slits do. In addition to their use as novelty items, diffraction gratings are commonly used for spectroscopic dispersion and analysis of light. Diffraction gratings work both for transmission of light, as in Figure 2, and for reflection of light, as on butterfly wings and the Australian opal in Figure 3 or the CD in Figure 1. These can be photographically mass produced rather cheaply. A diffraction grating can be manufactured by scratching glass with a sharp tool in a number of precisely positioned parallel lines, with the untouched regions acting like slits. An interference pattern is created that is very similar to the one formed by a double slit (see Figure 2). (credit: Infopro, Wikimedia Commons)Īn interesting thing happens if you pass light through a large number of evenly spaced parallel slits, called a diffraction grating. Colors such as these are direct evidence of the wave character of light. The colors reflected by this compact disc vary with angle and are not caused by pigments. Discuss, both qualitatively and quantitatively theĬhallenges associated with making Blue-ray discs and Blue-ray readers.Figure 1. Holds 700 Megabytes of data, determine the storage capacity of a DVD.Ĭheck your results. Įxplain carefully how you arrived at your prediction. Extrapolateįrom your results to predict a storage ratio. Your results), determine the track spacing on the CD and DVD. Using two different color lasers (average

You will need to reflect a laser off of the surface to see the Should be able to remove a small area of the coating. By scraping the CD surface and then applying strong tape, you The main challenge is that both CDs and DVDs haveĬoatings. Track separation (using the same process as you used for finding the thickness Should be able to produce a diffraction pattern and use it to determine the By shining a laser on one of the discs, you Procedure: At your station you should find In CDs and DVDs and deduce the ratio of their storage capacities. Of this exploration is to use laser diffraction to measure the track separation Most modern computers have opticalĭrives that use lasers to read information from spinning discs.
Dvd groove spacing light diffraction portable#
You should also include all derivations of the formulas governing this phenomena that you used to deduce the hair/wire thickness.Ĭompact Discs and DVDs are the most common and least expensive portable storage Your report should include a carefully written discussion of Single Slit Interference, including diagrams showing how light interferes to create the patterns you observed in the lab. For each, you will need to explain exactly how you deduced the thickness from the fringe spacings and the geometry of your setup. Measure the thickness of two different thin wires/hairs. Once you have done this, you should be able to use your results to determine the thickness of hair/wire you used. Once you understand the theory behind a single slit diffraction pattern (which is different from a double slit interference pattern), you will need to deduce analytically/mathematically the connection between the light/dark fringe spacings and the thickness of the hair. Your group should research "Single Slit Interference". Unlike the other labs this this quarter, this lab requires you to research the observed phenomena independently. Diffraction Pattern made by shining a Laser on a Hair


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
